While protecting individuals from colon cancer, a colonoscopy is an essential medical procedure. Unfortunately, going through this procedure can seem daunting for those who suffer from hemorrhoids.
A colonoscopy procedure allows your physician to check for the presence of hemorrhoids. They're also likely to recommend several strategies to help you to remain comfortable during the process. For managing hemorrhoid discomfort before or after the procedure, products like Dr. Numb numbing cream can provide temporary relief from pain and irritation.
This blog post discusses gastroenterologists' role in treating hemorrhoids during colonoscopies, the risks and benefits of colonoscopy with hemorrhoids, and the role of hemorrhoids during colonoscopy.
Key Takeways
- A colonoscopy is a vital medical procedure capable of detecting colon abnormalities, including colon cancer, and is considered the gold standard for such diagnoses.
- People with hemorrhoids might find the colonoscopy process challenging. However, gastroenterologists can guide preparations, manage discomfort, and even remove hemorrhoids during the procedure.
- It's crucial to inform your physician about hemorrhoids before a colonoscopy to prevent complications like excessive bleeding or perforation during the procedure.
- Hemorrhoid removal during a colonoscopy, termed hemorrhoid banding, is only recommended for significant bleeding or discomfort.
- Aftercare following a colonoscopy is vital to prevent hemorrhoids from worsening. This might include sitz baths, topical creams, or other recommended treatments.
- The colonoscopy prep can exacerbate hemorrhoids due to increased bowel movements, dehydration, straining, or use of enemas or suppositories.
- After a colonoscopy, some patients might experience hemorrhoid discomfort. Several home remedies and over-the-counter treatments are available to manage symptoms.
- Hemorrhoid banding can be performed during a colonoscopy, offering a minimally invasive treatment option with quick recovery time.
Hemorrhoids During Colonoscopy: Risks & Benefits

The benefits of a colonoscopy for preventative health reasons far outweigh the risks of having hemorrhoids. Colonoscopy is considered the gold standard for detecting colorectal cancer and other abnormalities in the colon. If detected early, these abnormalities can often be treated before they develop into cancer.
However, hemorrhoids can increase the risk of bleeding or perforation during the procedure. Therefore, it is essential to inform the gastroenterologist about the presence of hemorrhoids before undergoing a colonoscopy.
Hemorrhoid Removal During Colonoscopy: Is It Possible?
Hemorrhoids are a common condition that usually doesn't interfere with the colonoscopy procedure. In some cases, the gastroenterologist may remove hemorrhoids during a colonoscopy. This procedure is called hemorrhoid banding or rubber band ligation and involves placing a small rubber band around the base of the hemorrhoid to cut off its blood supply. The hemorrhoid then shrinks and falls off.
Hemorrhoid removal during colonoscopy is only recommended if the hemorrhoids are causing significant bleeding or discomfort and should only be performed by a trained professional.
Considerations For Hemorrhoids During Colonoscopy
If you have hemorrhoids and are planning to undergo a colonoscopy, there are a few things you should know:
- Talk to your doctor: If you have hemorrhoids, it is important to inform your doctor before the procedure. Your doctor may recommend certain medications or advise you to take measures to manage your hemorrhoids before the procedure.
- Prep for colonoscopy may cause more discomfort: The prep for colonoscopy, which involves drinking a liquid to empty the bowels, can cause more discomfort if you have hemorrhoids. However, there are ways to minimize the discomfort, such as using a sitz bath or applying a hemorrhoid cream before and after the prep.
- Colonoscopy may aggravate hemorrhoids: The insertion of the colonoscope can cause some discomfort and irritate the hemorrhoids. However, your doctor can apply a local anesthetic or prescribe a pain medication to help manage the discomfort.
- Hemorrhoids can be removed during colonoscopy: In some cases, hemorrhoids can be removed during the colonoscopy procedure. However, this is only recommended if the hemorrhoids are causing significant discomfort or bleeding. Your doctor will discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with you before recommending it.
- Aftercare is important: After the procedure, it is important to take care of your hemorrhoids to prevent them from getting worse. Your doctor may recommend a sitz bath, topical creams, or other measures to manage the discomfort and promote healing.
How Do Gastroenterologists Treat Hemorrhoids During Colonoscopies?

Gastroenterologists play a critical role in treating and managing hemorrhoids during colonoscopies. They can guide how to prepare for a colonoscopy and manage hemorrhoid discomfort.
Gastroenterologists can also perform hemorrhoid removal procedures during a colonoscopy or refer patients to a specialist for more advanced treatment. The key is for patients to communicate openly and honestly with their gastroenterologist about any symptoms or concerns before a colonoscopy.
Colonoscopy Procedure With Hemorrhoids
A colonoscopy involves examining the large intestine for abnormalities using a slender, flexible tube. In this deep dive, we'll explore how the procedure is performed and what happens afterward, discussing how colonoscopies can flag hemorrhoids.
Necessary preparations for the procedure
Before undergoing a colonoscopy, it is crucial to inform your physician of any health issues you may have, such as hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower rectum or anus that can cause discomfort or pain.
Sometimes, hemorrhoids can bleed, leading to anemia and other health complications. Therefore, if you have hemorrhoids, discussing their presence before the procedure is essential to ensure that necessary precautions are taken.

How is a colonoscopy performed?
During a colonoscopy, a long, flexible tube with a camera called a colonoscope is inserted through the rectum and into the colon. The camera transmits images of the colon to a monitor, allowing the physician to examine the tissues and detect any abnormalities.
While performing the procedure, the physician will carefully navigate the scope around any hemorrhoids that may be present to avoid causing discomfort or aggravating the hemorrhoids.
What Happens After The Procedure?
After a colonoscopy, patients may experience bloating, cramping, or mild pain. If hemorrhoids were detected during the procedure, the patient may experience increased discomfort and bleeding, typically temporary.
Patients should follow all post-operative instructions, including avoiding strenuous activity and heavy lifting, to prevent complications and promote proper healing of any hemorrhoids.
Detection of Hemorrhoids During a Colonoscopy
Hemorrhoids can be detected during a colonoscopy, and their presence is not uncommon. The physician will carefully examine the tissues of the rectum and colon to identify any swollen veins or abnormal tissue growths.
If hemorrhoids are detected, the physician will make a note in the patient's medical records and may recommend further evaluation or treatment after the procedure. It is crucial to discuss any findings with your physician to ensure appropriate care is taken for any health issues, including hemorrhoids.
Factors Contributing to Hemorrhoids During Colonoscopy Prep
- Increased Bowel Movements: Colonoscopy prep often involves consuming large volumes of liquid laxatives or solutions to clear the colon. This can lead to more frequent bowel movements, potentially causing irritation and strain on the anal area, which may aggravate existing hemorrhoids or contribute to the formation of new ones.
- Dehydration: The fasting and purging associated with colonoscopy prep can lead to dehydration if adequate fluids are not consumed. Dehydration can cause harder stools, which may require increased straining during bowel movements, further irritating hemorrhoids or causing them to develop.
- Straining: The urgency to clear the colon quickly during prep can sometimes lead to straining during bowel movements. Straining puts pressure on the veins in the rectal area, potentially exacerbating hemorrhoids or causing them to bleed.
- Use of Enemas or Suppositories: In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend enemas or suppositories to help cleanse the colon before a colonoscopy. These methods can irritate the rectal area and may contribute to discomfort or aggravate existing hemorrhoids.
Is it Possible To Diagnose Hemorrhoids With a Colonoscopy?
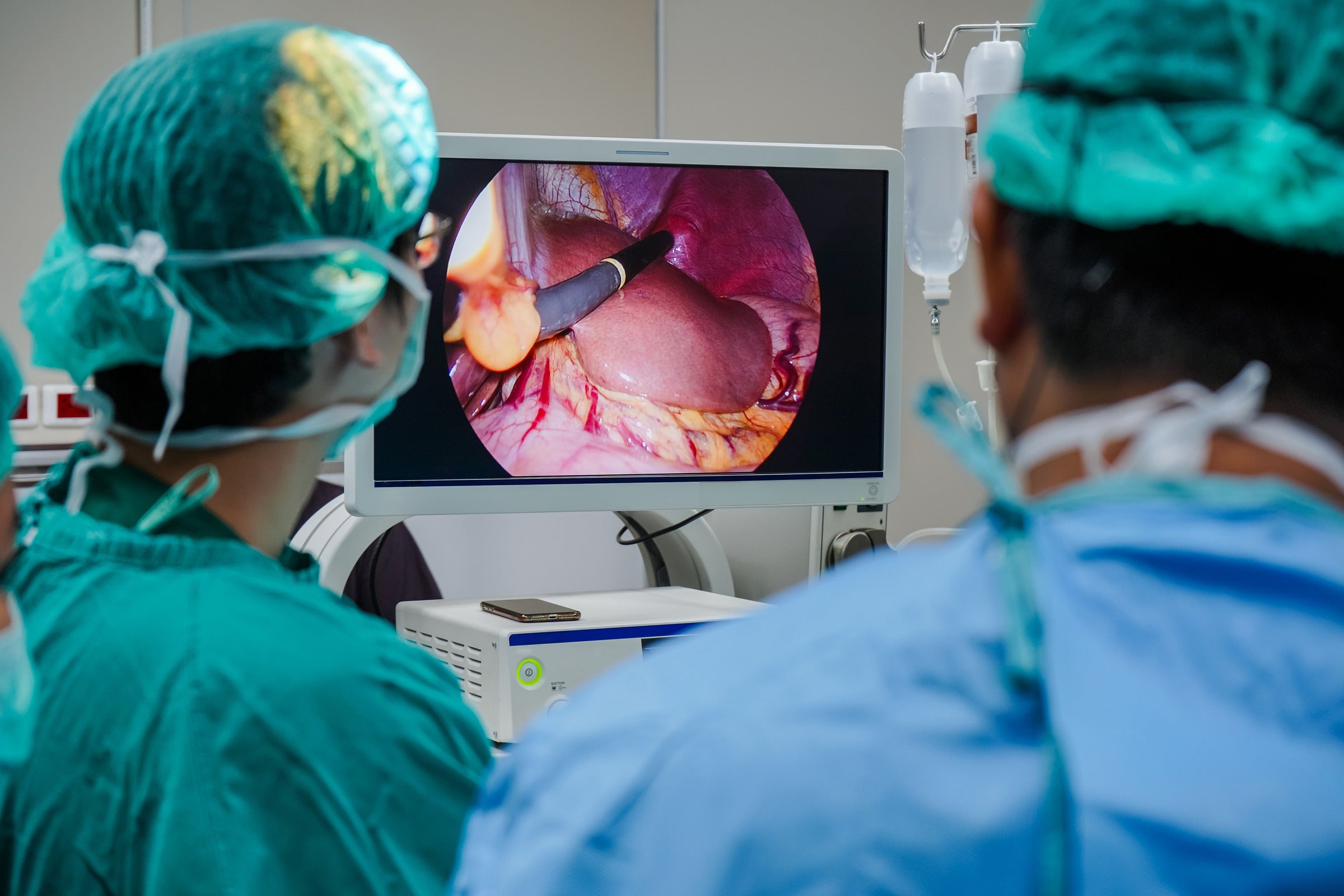
Hemorrhoids are a common medical condition and can cause discomfort and pain. They are swollen veins in the rectal or anal area that can cause bleeding, itching, and pain during bowel movements.
A colonoscopy is a medical procedure that involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera into the rectum and colon to examine the colon's lining. A colonoscopy is not typically used to diagnose hemorrhoids.
However, if the colonoscopy shows any signs of bleeding, the doctor may perform additional tests to determine the cause and rule out other conditions. These tests may include anorectal manometry, anal ultrasound, or sigmoidoscopy.
In What Cases Should One Avoid Getting A Colonoscopy?
A colonoscopy is a safe and effective way of detecting colon cancer and polyps. However, there are certain situations in which a colonoscopy should be avoided.
- A colonoscopy should not be performed if an individual has a perforated bowel or severe bleeding.
- If an individual has a history of severe heart or lung disease, the risks of sedation and complications associated with colonoscopy may outweigh the benefits.
- A colonoscopy should be avoided if an individual is pregnant because of the potential harm to the developing fetus.
- If an individual has had a recent colonoscopy and no follow-up is necessary, there is no need for another colonoscopy.
Hemorrhoids After Colonoscopy
After a colonoscopy, it is possible to experience the discomfort of hemorrhoids. Luckily, various preventive measures, treatments, and home remedies alleviate the pain and prevent future occurrences.

Possible Complications After Colonoscopy With Hemorrhoids
Although hemorrhoids during colonoscopy are a common occurrence, in some cases, they may lead to complications. These complications may include bleeding, infection, and severe pain. In rare cases, hemorrhoids may become thrombosed, meaning that a blood clot develops within the hemorrhoid tissue, leading to severe pain and swelling.
If a patient experiences excessive bleeding after a colonoscopy, they should seek medical attention immediately. Infection may occur due to poor hygiene, and it can be prevented through proper cleaning and care of the anal area following the procedure. Pain management is essential to preventing complications after colonoscopy, especially in hemorrhage patients.
Home Remedies And Treatments For Hemorrhoids After Colonoscopy
Home remedies can be effective in treating external hemorrhoids. One can try sitting in a warm bath to soothe an irritated hemorrhoid. Making lifestyle changes such as avoiding sitting and straining on the toilet for long periods and ensuring that stool moves along can also make a difference. It is suggested to increase dietary fiber intake and use stool softeners.
While some patients may experience mild hemorrhoid symptoms that resolve independently, others may require treatment for more severe cases. Various home remedies and over-the-counter treatments can be used to manage hemorrhoid pain and discomfort after colonoscopy.
Sitz baths and ice packs are popular remedies for hemorrhoid pain, as they help reduce swelling, inflammation, and discomfort. Over-the-counter creams and ointments that contain witch hazel, hydrocortisone, or numbing agents can also be used. In some cases, if hemorrhoids are very large or painful, a minimally invasive procedure may be necessary to remove them.
Treatment And Prevention Of Hemorrhoid Pain After Colonoscopy
After a colonoscopy, the prevention and treatment of hemorrhoids can be achieved by following certain precautions. Patients should maintain good hygiene, avoid straining during bowel movements, and keep the anal area clean and dry.
A doctor may recommend a stool softener or laxative to prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements. Patients should seek medical attention immediately if hemorrhoid pain persists or becomes severe.
And prescription-strength pain medication, topical creams, or minimally invasive procedures to alleviate the symptoms. Patients can manage their hemorrhoid pain after a colonoscopy and prevent future complications with proper prevention and treatment.
Hemorrhoid Banding During Colonoscopy

During a colonoscopy, doctors perform hemorrhoid banding to treat the condition. The procedure involves placing a small band around the hemorrhoid to cut off blood circulation and shrink the tissue. Hemorrhoid banding is a beneficial treatment option for those suffering from hemorrhoids as it is minimally invasive and has a faster recovery time than other procedures.
Performing Hemorrhoid Banding During Colonoscop
Hemorrhoid banding can be performed during a colonoscopy using an anoscope that allows the doctor to see inside the anus and rectum. The procedure involves identifying hemorrhoid and wrapping a rubber band around its base. The band cuts off the blood supply to the hemorrhoid, causing it to shrink and disappear. There is no need for anesthesia, and the procedure can be outpatient.

Benefits of Hemorrhoid Banding During Colonoscopy
There are several advantages to using hemorrhoid banding alongside a colonoscopy.
- This procedure is minimally invasive and can replace the need for surgery.
- During a colonoscopy, doctors can examine the entire colon and look for other conditions while treating the hemorrhoids, making for a more inclusive procedure.
- You can avoid hospitalization and healing time since it is an outpatient procedure.
- The risks associated with the procedure are much lower than surgical alternatives.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, hemorrhoids can make the colonoscopy procedure uncomfortable and sometimes painful. However, the procedure can still be safely conducted with proper preparation and treatment. Gastroenterologists are crucial in treating hemorrhoids during colonoscopies and relieving patients from hemorrhoid pain.
Detecting hemorrhoids during a colonoscopy could save patients from further discomfort and medical attention. If you have hemorrhoids and are scheduled for a colonoscopy, speak with your doctor about preparing and managing your hemorrhoids before and after the procedure.