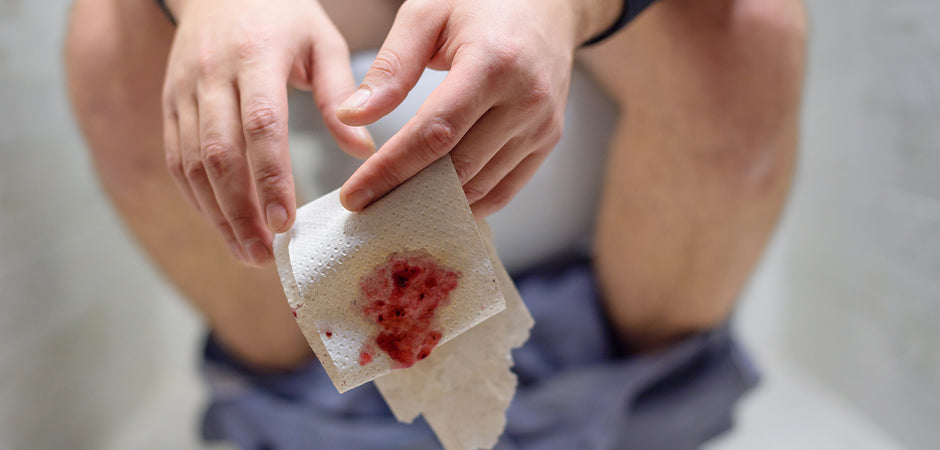
The bleeding caused by internal hemorrhoids is usually bright red and brisk. It can appear on toilet paper, dribble into the toilet bowl, or streak on the stool. Symptomatic hemorrhoids do not always result in significant bleeding.
Yes, the hemorrhoids are swollen blood vessels in the rectum or anus that are painful, itchy, and occasionally make you bleed. Blood can stain toilet paper, coat stool, or drip into the toilet after bowel movement when hemorrhoids are present.
This blog post will explore the signs and symptoms of hemorrhoid bleeding, how to diagnose and treat the condition, how to prevent it, and potential complications.
Can You Bleed From A Hemorrhoid: 5 Signs And Symptoms

Hemorrhoids are common medical conditions, particularly among people aged 45 to 65. Symptoms of hemorrhoid bleeding include bright red blood in the toilet bowl. Rectal bleeding, discomfort, and pain characterize this condition.
Rectal Bleeding
Hemorrhoid bleeding is most visible in the rectal area. Rectal hemorrhoid bleeding looks like bright red, dark red, or maroon. Blood may be observed on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl. If you see a small amount of bright red blood on the toilet paper after wiping, it is a sign of minor rectal bleeding. If hemorrhoid bleeding occurs, it can lead to pain, discomfort, and itching, which can have bad effects.
Blood in Stool
Hemorrhoids are also characterized by blood in the stool. Blood streaks may appear on the seat, and blood may be mixed with feces to make the chair look black.
Itching And Irritation Around the Anus
Around the anus, hemorrhoid bleeding can also cause itching and irritation. The itching can be intense, and it can be challenging to find relief. It is possible to aggravate the condition by scratching and causing more Bleeding.
Pain During Bowel Movements

Hemorrhoid bleeding can also cause pain during bowel movements. The pain caused by hemorrhoids depends on the severity and can be mild or intense. The pain may persist even after the bowel movement has ended.
Swelling or Lumps Around The Anus
Hemorrhoid bleeding is often accompanied by anus swelling or lumps. These swollen veins can cause discomfort and itching and may occur internally or externally depending on their location within the rectum or just outside the opening of the anus.
A thorough understanding of hemorrhoid bleeding symptoms is essential to prevent further complications.

Hemorrhoid Bleeding: 3 Diagnosis
There are a variety of underlying causes for hemorrhoid bleeding. Blood is lost from the rectum, anal canal, or lower gastrointestinal tract. Hemorrhoids comprise swollen and inflamed veins in the anus or rectum, which causes hemorrhages.
Anorectal exam
Healthcare providers perform examinations to diagnose abnormalities in a patient's rectal and anal areas. The healthcare provider inserts their finger into the rectum during the digital rectal exam to feel for hemorrhoids, fissures, or other abnormalities.
Sigmoidoscopy or Colonoscopy

A sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy is a diagnostic confirmatory test used to check the rectum and colon for exceptions, including hemorrhoids. During a sigmoidoscopy, a flexible tube containing a video camera is passed through the lower colon to observe it.
A colonoscopy uses a longer line to view the entire colon. These procedures can help to diagnose the severity and location of hemorrhoids causing bleeding. They are very effective in evaluating gastrointestinal bleeding and identifying the underlying cause. Heres some definitions of gi bleed or hemorrhage vs hemorrhoid
Gastrointestinal Bleeding (GI Bleeding)
- Definition: Bleeding in any part of the GI tract.
- Symptoms: Bright red or dark blood in stool. Shortness of breath, and abdominal pain.
- Causes: Ulcers, inflammation, injuries, etc.
- Severity: Can be mild to life-threatening.
- Treatment: Depends on the cause; may require medical intervention.
Hemorrhoids
- Definition: Swollen veins in the lower rectum or anus.
- Symptoms: Bright red blood in stool. Itching or pain around the anus, swelling or a lump near the anus.
- Causes: Straining during bowel movements, increased pressure because of pregnancy, etc.
- Severity: Usually not severe, but can lead to complications if untreated.
- Treatment: Often resolves with home care; persistent or severe cases may require medical procedures.
Stool Analysis
Stool analysis is an essential diagnostic tool for detecting the presence of gastrointestinal bleeding, including that caused by hemorrhoids. Blood in the stool can be determined by performing a simple fecal occult blood test, which indicates hemorrhoids or an underlying medical condition.
This non-invasive screening test is widely available, cost-effective, and highly accurate, making it an integral part of the diagnostic process. Furthermore, it can help detect early-stage hemorrhoids and prevent more severe complications by enabling prompt treatment.
Hemorrhoid Bleeding: 2 Treatment Methods
Hemorrhoid bleeding is a common problem faced by a large population, especially the elderly. When the veins in the rectal area swell and become irritated or burst, bleeding during bowel movements occurs. Hemorrhoid bleeding is not life-threatening but can cause significant discomfort and pain. Here, some treatment options are explained.

Non-Surgical Treatments
- An over-the-counter cream or suppository containing hydrocortisone, a steroid that reduces inflammation. Directly applied to the affected area, they relieve discomfort.
- Hemorrhoid pads containing witch hazel, a natural astringent that shrinks swollen blood vessels and reduces itching. Additional relief can be achieved with these pads.
- Numbing agents for those experiencing significant pain. Local anesthetic creams can be applied topically to relieve discomfort.
- It is important to note that these non-surgical treatments do not address the underlying cause of hemorrhoids.
- Persistent or severe cases should seek medical attention to determine the best treatment options.
Surgical Treatment
- Surgical treatment for hemorrhoid bleeding involves a procedure known as the stapled hemorrhoidopexy.
- This technique is usually reserved for internal hemorrhoids as it blocks blood flow to the hemorrhoidal tissue, causing it to shrink.
- The stapled hemorrhoidopexy is less painful than the more invasive hemorrhoidectomy, enabling an earlier return to regular activities.
- Circular staplers remove mucosa above hemorrhoidal tissue and pull the remaining tissue into its normal position.
- As opposed to traditional surgery, stapled hemorrhoidopexy offers quicker recovery times, less postoperative discomfort, and fewer complications.
- A qualified healthcare provider should always be consulted to determine whether the procedure suits a hemorrhoid patient.
- Stapled hemorrhoidopexy is an effective solution for hemorrhoids when performed correctly.
Hemorrhoid Bleeding: 3 Prevention
External and internal hemorrhoids often cause hemorrhoid bleeding. When a hemorrhoid is strained or passed through a tough stool, the surface is damaged, resulting in external hemorrhoid bleeding. Despite not being a severe illness, it can be uncomfortable and alarming for those who experience it. The good news is that several measures can prevent hemorrhoid bleeding.
Regular Hemorrhoid Exercise

Regular exercise can be vital in managing hemorrhoids, promoting better circulation, and reducing discomfort. By incorporating specific exercises into your routine, you can strengthen the muscles in the affected area and ease symptoms. Stay active and consider tailored workouts to support your hemorrhoid treatment plan.
- Yoga poses can provide relief for hemorrhoid-related issues.
- Viparita Karani, or the legs-up-the-wall pose, can help alleviate pressure and reduce irritation and pain.
- To do this pose, lie on your back close to a wall, extending your legs up with your hips touching and legs straight.
- Yoga posture Sarvangasana, or shoulder stand, stimulates the organs in the rectal area and increases blood flow.
- To do this pose, lay flat on your back and lift both legs over your head.
- Sirsasana, or the headstand pose, can also aid in reducing swelling and pain caused by hemorrhoid bleeding.
- This pose increases blood flow to the lower body, reduces stress and anxiety, and stimulates digestion.
- Practicing these poses and hemorrhoid treatment can improve overall wellness and quality of life for people with hemorrhoids.

Avoiding Straining During Bowel Movements
- Straining during bowel movements is the leading cause of hemorrhoid bleeding.
- Excessive pressure on the rectal veins can cause them to swell and hemorrhage.
- Fiber-rich diets and hydration can improve stool softness and ease bowel movements, helping to avoid straining.
- A stool softener or laxative can make bowel movements more comfortable and prevent straining.
- Using a footstool to elevate one's legs when sitting on the toilet can facilitate proper bowel movement and reduce straining.
- It is essential to avoid using laxatives indiscriminately and consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and treatment.
- Regular exercise and physical activity, like walking and yoga, can also help improve bowel regularity and prevent straining.
- Certain medications, like opioids, can contribute to constipation and straining, so adjusting medications or seeking alternative treatments may be necessary.
- Surgical intervention may be necessary for severe hemorrhoids or persistent difficulty with bowel movements.
Practicing Good Anal Hygiene

- Good anal hygiene is essential in preventing hemorrhoid bleeding.
- Wiping the anal area gently with moistened or soft toilet paper after bowel movements to feel Numb.
- Excessive wiping or using rough toilet paper can irritate the anus and worsen hemorrhoid symptoms.
- Sit in a sitz bath and apply warm compresses to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Avoid using irritating soaps or cleansers on the anal area.
- Regular exercise is recommended to prevent hemorrhoid bleeding.
- Straining during bowel movements should be avoided to prevent the worsening of hemorrhoid symptoms.
- Adopting good anal hygiene and preventative measures can minimize the recurrence of hemorrhoids.
- Seeking medical attention is necessary if bleeding persists or worsens despite these preventative measures.
By following these few key steps consistently and incorporating them into your daily routine, you will observe noticeable signs of healing from your hemorrhoids. It's important to be patient and allow time for the healing process to take effect.
Hemorrhoid Bleeding: 4 Potential Complications
Hemorrhoid bleeding can lead to anemia due to blood loss. In severe cases, the hemorrhoids may also develop blood clots or thrombosis. Medical treatment may be necessary as a result of this type of pain.
Anemia
One of the potential complications of hemorrhoid bleeding is anemia. Anemia occurs when a person's blood inadequately carries oxygen to their organs. The blood loss from hemorrhoids can cause anemia, which can be severe in some cases.
Anemia symptoms include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, pale skin, and chest pain. Get medical attention if you experience these symptoms. Boosting your daily fiber intake is crucial for anemia treatment.

Infection
Another potential complication of hemorrhoid bleeding is an infection. Bacteria can enter the bloodstream when the skin is broken and exposed to fecal matter.
Symptoms of an infection include fever, chills, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Self-treating the infection can cause further complications, so seek medical attention immediately.
Blood Clots
Hemorrhoid bleeding can also lead to blood clots. Anus or rectum blood clots can cause discomfort, pain, and difficulties passing stool. Sometimes, blood clots can travel to other body parts and cause serious health problems. A bowel movement that contains blood clots should be investigated.
Strangulated Hemorrhoids

A strangulated hemorrhoid is one of the most serious complications of hemorrhoid bleeding. Strangulated hemorrhoids happen when the anal sphincter cuts off the blood supply.
Conclusion
Symptoms of hemorrhoids include hemorrhoid bleeding. Symptoms such as persistent bleeding or other concerning symptoms need immediate medical attention, even if not severe.
Being proactive about your health is crucial, so don't hesitate to see your doctor for treatment. You will receive immediate relief and avoid complications affecting your overall health.