Allergy shots are immunotherapy that enhances your immune system's ability to tolerate allergens. The medications can help reduce symptoms, but they are not a cure for allergies and may not work for everyone. Talk to your doctor to see if they are a good option .
Hives, sneezing, and nasal congestion are all possibilities. More severe reactions include throat swelling, wheezing, redness, and chest tightness. An allergic reaction called anaphylaxis is rare, but it can be deadly. Blood pressure can drop, and breathing can be challenging.
Side Effects of Allergy Shots In Adults: 7 Expected Reactions

Allergy shots, also known as immunotherapy, are used to treat allergies. However, like any medical procedure, they come with potential side effects and reactions that you should understand. Here are some expected responses to allergy shots in adults:
Local Reactions
Local reactions are the most common side effects of allergy shots. These reactions typically occur at the site of the injection and can appear within a few hours of receiving the shot.
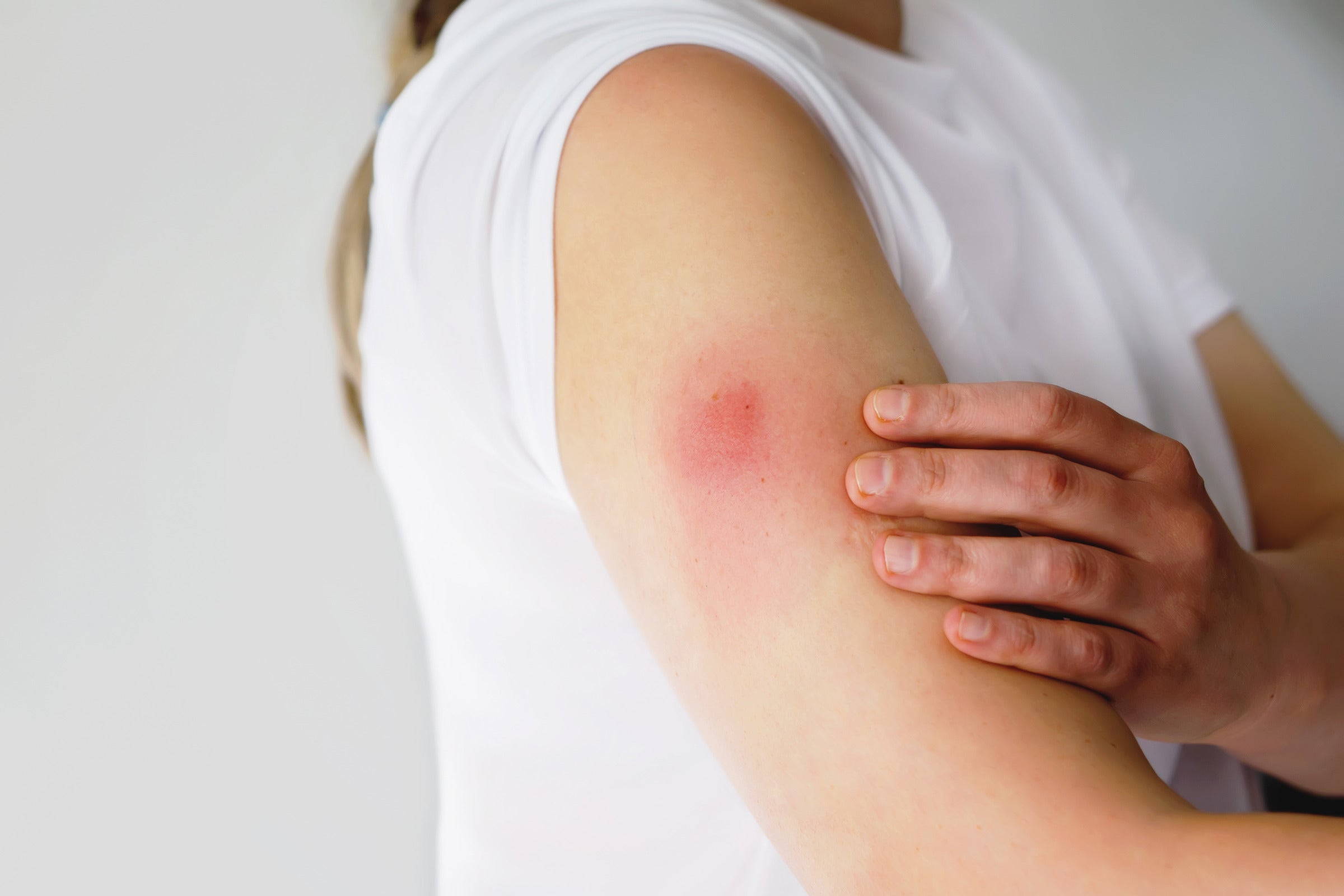
Injection Site Redness, Swelling
One of the most common local reactions to allergy shots is redness, swelling, and itching at the injection site. This reaction can look similar to hives or mosquito bites. The area around the injection site might also swell into a more significant bump. Most of these symptoms go away in a few hours or days.
Nasal Congestion and Sneezing
Some individuals may experience nasal congestion and sneezing after receiving an allergy shot. These symptoms are usually temporary and resolve on their own. If they persist, it's recommended that they consult with a healthcare professional.

Systemic Reactions
Allergy shots are immunotherapy that can cause local and systemic reactions, including anaphylaxis. They are typically recommended to reduce symptoms when medications are insufficient for individuals with allergies. Systemic reactions involve the entire body and are less common than local reactions. They usually occur within minutes to hours after receiving the shot.
Itchy Skin and Hives
Itchy skin and hives are systemic reactions that can occur after an allergy shot. Symptoms of hives include red, raised bumps anywhere on your body. They can cause discomfort but are usually not serious. However, if hives cover a large body area or persist for more than a day, seeking medical attention is essential.
Stuffy Nose
A stuffy nose, also called nasal congestion, is another systemic reaction that can occur after receiving an allergy shot. A runny nose and sneezing might accompany this symptom. Over-the-counter decongestants can help ease these symptoms.
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis symptoms can start minutes after receiving the shot and may be accompanied by swelling in the throat, wheezing, and nausea. Other symptoms may include a rapid heartbeat, a sudden feeling of warmth, and a severe rash.
People Who Should and Shouldn't Get Allergy Shots

The allergy shot, also called allergen immunotherapy, is a standard treatment for various types of allergies. However, they're only suitable for some. This article explores when to consider allergy shots, who should avoid them, and what allergies they can treat.
Pregnant women
Pregnancy can alter the body's immune response, potentially affecting how one responds to allergy shots. Therefore, it's recommended that pregnant individuals avoid starting allergy shot therapy. However, those who were already receiving allergy shots before becoming pregnant may continue their treatment under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
People with Heart Disease
Patients with heart disease may face increased risks from allergy shots, especially if they have uncontrolled hypertension or ischemic heart disease. This is because severe allergic reactions could significantly strain the heart.

People with Severe Asthma
Severe asthma can be exacerbated by allergy shots. If asthma symptoms are not well-controlled, allergic reactions to the shots could trigger severe asthma attacks.
When Should You Consider Allergy Shots?
Many people can benefit from allergy shots, especially those with certain conditions.
- Allergic Rhinitis: Could also be called hay fever, can be effectively managed with allergy shots.
- Eye Allergies (Allergic Conjunctivitis): Allergy shots can help manage symptoms such as itchy, red, and watery eyes.
- Insect Allergies: Allergy shots can reduce the risk of severe allergic reactions, particularly for those allergic to bees and other stinging insects.
- Medications Don't Control Symptoms Well: If allergy medications aren't effectively controlling your symptoms or can't avoid the allergens causing your reactions, allergy shots might be a good option.
- Allergy Medications Interact with Other Drugs: If you're taking other medications that interact negatively with allergy medications, or if allergy medications cause bothersome side effects, consider discussing allergy shots with your healthcare provider.
- To Reduce Long-Term Use of Allergy Medication: Allergy shots might reduce your reliance on daily allergy medication by helping your body build a tolerance to allergens.
Allergy Shots Work Process
An allergy shot is a long-term treatment approach designed to decrease your sensitivity to allergens. It's a two-phase process: the buildup phase and the maintenance phase. The purpose, duration, and frequency of each phase will be explained.
Buildup Phase of Allergy Shots
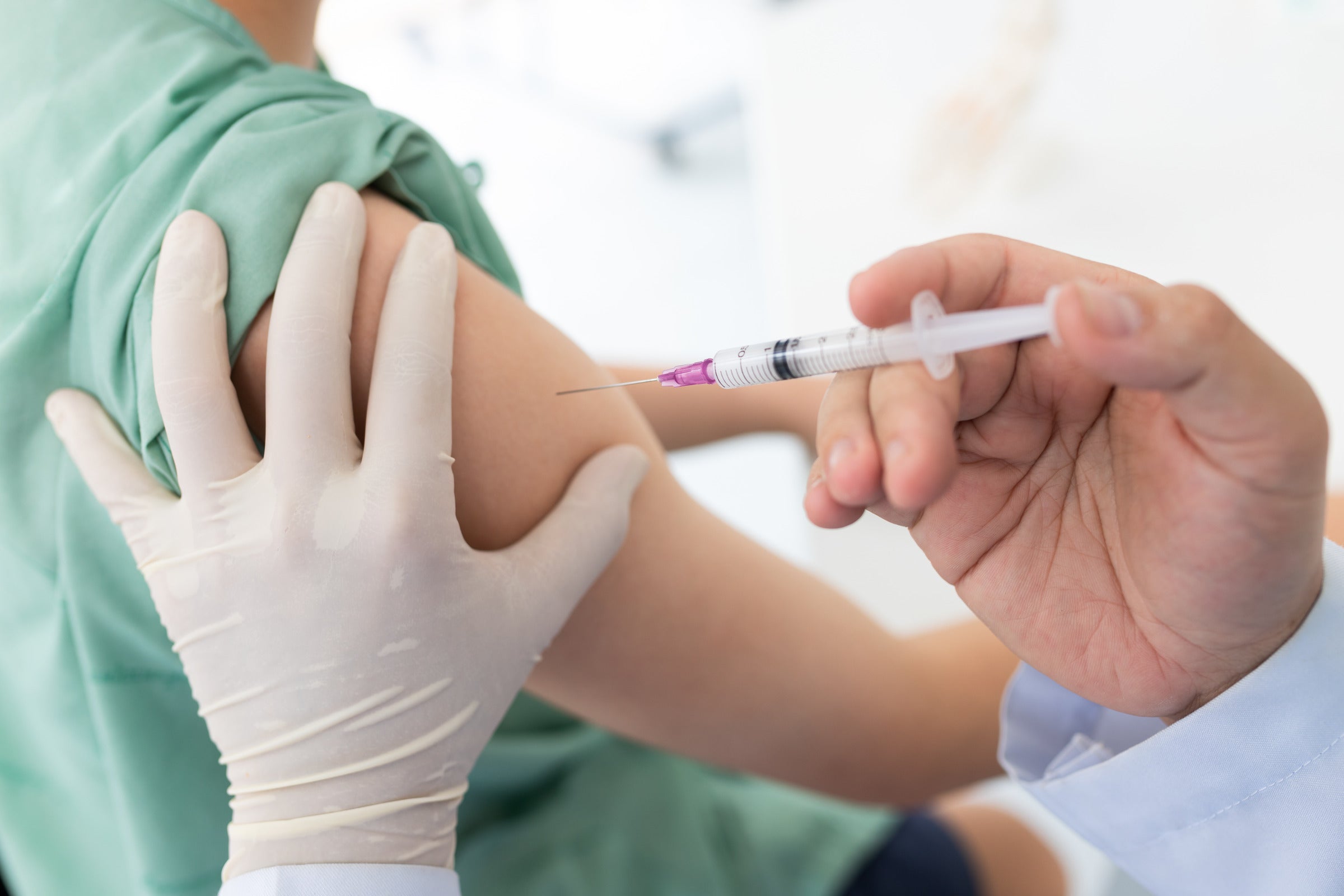
The buildup phase is the initial stage of allergen immunotherapy. During this phase, the dose of allergens in the shots gradually increases to help your immune system build tolerance. Here's what you need to know:
- Duration: The buildup phase lasts three to six months.
- Frequency: Typically, shots are administered one to three times a week.
- Dosage Increase: The allergen dose is increased incrementally with each shot during the buildup phase.
- Goal: The buildup phase aims to accustom your immune system to the allergens, reducing your allergic reactions.
Maintenance Phase of Allergy Shots
After the buildup phase comes the maintenance phase. This phase involves regular injections over a prolonged period to maintain your immune system's tolerance to the allergens. Here are the key points:
- Duration: The maintenance phase usually lasts three to five years. The maintenance phase may extend beyond five years for those with severe allergies.
- Frequency: During this phase, allergy shots are typically given about once a month.
- Goal: The maintenance phase aims to sustain the immune system's tolerance to allergens, leading to a long-term reduction in allergy symptoms.

Conclusion
Allergy shots can effectively treat many adults suffering from robust allergic reactions. However, they are not without side effects, some of which can be severe. When deciding if allergy shots suit you, consider the benefits versus reactions.
Everyone's body is unique, and what works for some may not work for others. Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the best action for your health needs.
Keep in mind that these shots are an ongoing commitment that gradually helps your immune system build resilience against allergens. So, here's to your health and towards a more informed, allergy-free future.











![The Most Common Food Allergies That Cause Itchy Skin [6 Common Symptoms]](http://drnumb.com/cdn/shop/articles/Can_Food_Allergies_Cause_Itchy_Skin__17_Listed_6_Symptoms_Common.jpg?v=1714999986)


